CMS-01
CMS-01 is a communication satellite envisaged for providing services in Extended-C Band of the frequency spectrum. The Extended-C Band coverage will include Indian mainland, Andaman-Nicobar & Lakshadweep Islands. CMS-01 is the 42nd Communication Satellite of India.
CMS-01
GSAT-30
GSAT-30 is configured on ISRO’s enhanced I-3K Bus structure to provide communication services from Geostationary orbit in C and Ku bands. The satellite derives its heritage from ISRO’s earlier INSAT/GSAT satellite series. Weighing 3357 kg, GSAT-30 is to serve as replacement to INSAT-4A spacecraft services with enhanced coverage. The satellite provides Indian mainland and islands coverage in Ku-band and extended coverage in C-band covering Gulf countries, a large number of Asian countries and Australia
GSAT-30
GSAT-31
India’s telecommunication satellite, GSAT-31 was successfully launched on February 06, 2019 from Kourou launch base, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-247. GSAT-31 is configured on ISRO’s enhanced I-2K Bus, utilising the maximum bus capabilities of this type. This satellite will augment the Ku-band transponder capacity in Geostationary Orbit. Weighing about 2536 kg, GSAT-31 will provide continuity to operational services on some of the in-orbit satellites. The satellite derives its heritage from ISRO’s earlier INSAT/GSAT satellite series. The satellite provides Indian mainland and island coverage. The designed in-orbit operational life of GSAT-31 is about 15 years.

GSAT-31
GSAT-7A
GSAT-7A is the 35th Indian Communication satellite built by ISRO. GSAT-7A Spacecraft is configured on ISRO’s standard I-2000 Kg (I-2K) Bus. The Satellite is built to provide communication capability to the users in Ku-band over the Indian region.
GSAT-7A
GSAT-11
India’s next generation high throughput communication satellite, GSAT-11 was successfully launched on December 05, 2018 from Kourou launch base, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-246. Weighing about 5854 kg, GSAT-11 is the heaviest satellite built by ISRO. GSAT-11 is the fore-runner in the series of advanced communication satellites with multi-spot beam antenna coverage over Indian mainland and Islands. GSAT-11 will play a vital role in providing broadband services across the country. It will also provide a platform to demonstrate new generation applications. GSAT-11 was launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit and subsequently ISRO's Master Control Facility at Hassan taken over the control of GSAT-11 to perform the initial orbit raising maneuvers using the Liquid Apogee Motor of the satellite for placing it in circular Geostationary Orbit

GSAT-11
GSAT-29
GSAT-29 carries Ka/Ku-band high throughput communication transponders which will bridge the digital divide of users including those in Jammu & Kashmir and North Eastern regions of India. It also carries Q/V-band payload, configured for technology demonstration at higher frequency bands and Geo-stationary High Resolution Camera. carried onboard GSAT-29 spacecraft. An optical communication payload, for the first time, will be utilized for data transmission.

GSAT-29
GSAT-6A
GSAT-6A, similar to GSAT-6 is a high power S-band communication satellite configured around I-2K bus. The mission life of spacecraft planned is about 10 years. The satellite will also provide a platform for developing technologies such as demonstration of 6 m S-Band Unfurlable Antenna, handheld ground terminals and network management techniques that could be useful in satellite based mobile communication applications

GSAT-6A
GSAT-17
GSAT-17 is designed to provide continuity of services on operational satellites in C-band, Extended C-band and S-bands. GSAT-17 was launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) by Ariane-5 VA-238 launch vehicle. After its injection into GTO, ISRO's Master Control Facility (MCF) at Hassan takes control of GSAT-17 and performs the initial orbit raising maneuvers using the Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) of the satellite, placing it in circular Geostationary Orbit.

GSAT-17
GSAT-19
GSAT-19 satellite with a lift-off mass of 3136 kg, is the communication satellite of India, configured around the ISRO’s standard I-3K bus. GSAT-19 carries Ka/Ku-band high throughput communication transponders. Besides, it carries a Geostationary Radiation Spectrometer (GRASP) payload to monitor and study the nature of charged particles and the influence of space radiation on satellites and their electronic components. GSAT-19 also features certain advanced spacecraft technologies including miniaturised heat pipe, fibre optic gyro, Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) accelerometer, Ku-band TTC transponder, as well an indigenous Lithium-ion Battery.

GSAT-19
GSAT-9
GSLV-F09 launches 2230 kg South Asia Satellite GSAT-9 into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO). GSLV-F09 mission is the eleventh flight of India’s Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) and its fourth consecutive flight with the indigenous Cryogenic Upper Stage (CUS). The vehicle is designed to inject 2 - 2.5 ton class of satellites into GTO. The overall length of GSLV-F09 is 49.1 m. GSLV-F09 was launched on May 05, 2017 from the Second Launch Pad (SLP) at Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR (SDSC SHAR), Sriharikota, the space port of India. GSLV-F09 vehicle configuration including the CUS is similar to the ones successfully flown during the previous three missions – GSLV-D5, D6 and F05 – in January 2014, August 2015 and September 2016 respectively. GSLV-D5 and D6 successfully placed two communication satellites –GSAT-14 and GSAT-6, while GSLV-F05 placed India’s weather satellite INSAT-3DR, in the intended GTOs. S-band telemetry and C-band transponders enable GSLV-F09 performance monitoring, tracking, range safety/flight safety and Preliminary Orbit Determination (POD).

GSAT-9
GSAT-18
India's latest communication satellite, GSAT-18 was inducted into the INSAT/GSAT system on October 06, 2016 from Kourou, French Guiana by Ariane-5 VA-231. Weighing 3404 kg at lift-off, GSAT-18 carries 48 communication transponders to provide Services in Normal C-band, Upper Extended C-band and Ku-bands of the frequency spectrum. GSAT-18 carries Ku-band beacon as well to help in an accurately pointing ground antennas towards the satellite. GSAT-18 is designed to provide continuity of services on operational satellites in C-band, Extended C-band and Ku-bands. GSAT-18 was launched into a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO) by Ariane-5 VA-231 launch vehicle. After its injection into GTO, ISRO's Master Control Facility (MCF) at Hassan took control of GSAT-18 and performed the initial orbit raising maneuvers using the Liquid Apogee Motor (LAM) of the satellite, placing it in circular Geostationary Orbit. The designed in-orbit operational life of GSAT-18 is about 15 years.

GSAT-18
GSAT-15
GSAT-15, India’s latest Communication Satellite is a high power satellite being inducted into the INSAT/GSAT system. Weighing 3164 kg at lift-off, GSAT-15 carried a total of 24 communication transponders in Ku-band as well as a GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) payload operating in L1 and L5 bands. GSAT-15 is the third satellite to carry GAGAN payload after GAST-8 and GSAT-10, which are already providing navigation services from orbit. GSAT-15, carried a Ku-band beacon as well to help in accurately pointing ground antennas towards the satellite. GSAT-15 was launched by Ariane-5 VA-227 launch vehicle from Kourou, French Guiana on early morning of November 11, 2015

GSAT-15
GSAT-6
GSAT-6 is the twenty fifth geostationary communication satellite of India built by ISRO and twelfth in the GSAT series. Five of GSAT-6's predecessors were launched by GSLV during 2001, 2003, 2004, 2007 and 2014 respectively. After its commissioning, GSAT-6 joined the group of India's other operational geostationary satellites. GSAT-6 Satellite provides communication through S-band payload with five spot beams covering whole India for user links and C-band with one beam. The cuboid shaped GSAT-6 has a lift-off mass of 2117 kg. Of this, propellants weigh 1132 kg and the dry mass of the satellite is 985 kg. One of the advanced features of GSAT-6 satellite is its S-Band Unfurlable Antenna of 6 m diameter. This is the largest satellite antenna realised by ISRO. This antenna is utilised for five spot beams over the Indian main land. The spot beams exploit the frequency reuse scheme to increase frequency spectrum utilization efficiency. The other advanced feature of the satellite is the 70 V bus, which is flying first time in an Indian communication satellite

GSAT-6
GSAT-16
GSAT-16, an advanced communication satellite, weighing 3181.6 kg at lift-off, is being inducted into the INSAT-GSAT system. GSAT-16 is configured to carry a total of 48 communication transponders, the largest number of transponders carried by a communication satellite developed by ISRO so far, in normal C-band, upper extended C-band and Ku-band. GSAT-16 carried a Ku-band beacon as well to help accurately point ground antennas towards the satellite.

GSAT-16
GSAT-14
GSAT-14 is the twenty third geostationary communication satellite of India built by ISRO. The main objectives of GSAT-14 mission are To augment the In-orbit capacity of Extended C and Ku-band transponders and To provide a platform for new experiments.

GSAT-14
GSAT-7
GSAT-7 is an advanced communication satellite built by ISRO to provide wide range of service spectrum from low bit rate voice to high bit rate data communication. GSAT-7 Communication payload is designed to provide communication capabilities to users over a wide oceanic region including the Indian land-mass. The payload configuration is compatible with I-2.5K bus of ISRO. The GSAT-7 payload design includes Multiband communication.

GSAT-7
GSAT-10
GSAT-10, India’s advanced communication satellite, is a high power satellite being inducted into the INSAT system. Weighing 3400 kg at lift-off, GSAT-10 is configured to carry 30 communication transponders in normal C-band, lower extended C-band and Ku-band as well as a GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) payload operating in L1 and L5 bands. GSAT-10 is the second satellite to carry GAGAN payload after GSAT-8, which is already providing navigation services from orbit. GSAT-10 also carries a Ku-band beacon to help in accurately pointing ground antennas towards the satellite.

GSAT-10
GSAT-12
GSAT-12, the latest communication satellite built by ISRO, weighs about 1410 kg at lift-off. GSAT-12 was configured to carry 12 Extended C-band transponders to meet the country's growing demand for transponders in a short turn-around-time. The 12 Extended C-band transponders of GSAT-12 augments the capacity in the INSAT system for various communication services like Tele-education, Telemedicine and for Village Resource Centres (VRC).

GSAT-12
GSAT-8
GSAT-8, India’s advanced communication satellite, is a high power communication satellite being inducted in the INSAT system. Weighing about 3100 Kg at lift-off, GSAT-8 is configured to carry 24 high power transponders in Ku-band and a two-channel GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) payload operating in L1 and L5 bands. The 24 Ku band transponders will augment the capacity in the INSAT system. The GAGAN payload provides the Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS), through which the accuracy of the positioning information obtained from the GPS Satellite is improved by a network of ground based receivers and made available to the users in the country through the geostationary satellites.

GSAT-8
INSAT-4CR
INSAT–4CR spacecraft is configured with exclusive Ku band employing the I-2K Bus with a mass of 2130 Kg. It was injected into the orbit by GSLV-F04 rocket with enhanced Russian Cryogenic engine and co-located at 74o East longitude along with INSAT–3C / Kalpana–1 / GSAT–3 (EDUSAT). INSAT-4CR carries 12 high-power Ku-band transponders designed to provide Direct-to-home (DTH) television services, Video Picture Transmission (VPT) and Digital Satellite News Gathering (DSNG).

INSAT-4CR
INSAT-4B
INSAT–4B Spacecraft is the second in the INSAT 4 series of spacecrafts and is configured with exclusive communication payloads to provide services in Ku and C frequency bands. This is co-located with INSAT–3A at 93.5 o E longitude.

INSAT-4B
INSAT-4A
INSAT-4A, first in INSAT-4 Satellites series provides services in Ku and C-band frequency bands. The Ku transponders cover the Indian main land and C-Band transponders cover an extended area. It has a dozen Ku transponders and another dozen of C-band transponders. This spacecraft is placed at 83o E along with INSAT-2E and INSAT-3B, by Ariane launch vehicle (ARIANE5-V169).

INSAT-4A
GSAT-3
GSAT-3, known as EDUSAT is meant for distant class room education from school level to higher education. This was the first dedicated "Educational Satellite" that provide the country with satellite based two way communication to class room for delivering educational materials.

GSAT-3
INSAT-3E
INSAT-3E is the fourth satellite launched in the INSAT-3 series. It is an exclusive communication satellite to further augment the communication services that are being provided by the INSAT System. Weighing 2775 kg at lift-off, INSAT-3E carries 24 Normal C-band and 12 Extended C-band transponders.

INSAT-3E
GSAT-2
GSAT-2 is a 2000 kg class experimental communication satellite onboard the second developmental test flight of India's Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, GSLV-D2. The satellite carried four C-band transponders, two Ku-band transponders and a Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) payload operating in S-band and C-band for forward link and return link respectively. GSAT-2 also carried four scientific experimental payloads - Total Radiation Dose Monitor (TRDM), Surface Charge Monitor (SCM), Solar X-ray Spectrometer (SOXS) and Coherent Radio Beacon Experiment (CRABEX).

GSAT-2
INSAT-3A
INSAT–3A, the third satellite in INSAT–3 series is a multipurpose satellite for providing telecommunications, television broadcasting, meteorological and search and rescue services. It carries twenty four transponders – twelve operating in the normal C – band frequency, six in extended C-band and six in Ku–band. INSAT–3A also carries a Ku–band beacon. For Meteorological observation, INSAT–3A carries a three channel Very High Resolution Radiometer (VHRR). In addition, INSAT–3A carries a Charge Coupled Device (CCD) camera which operates in the visible and short wave infrared bands providing a spatial resolution of 1 km. A Data Relay Transponder (DRT) operating in UHF band is incorporated for real time hydro meteorological data collection from unattended located on land and river basins. The data is then relayed in extended C–band to a central location. INSAT–3A also carries another transponder for Satellite Aided Search and rescue (SA&R) as part of India’s contribution to the international Satellite Aided Search Programme.
INSAT-3A
INSAT-3C
INSAT-3C, carrying Fixed Satellite Services (FSS) transponders, Broadcast Satellite Services (BSS) transponders and Mobile Satellite Services (MSS) transponders is intended to continue the service of INSAT-2DT and INSAT-2C which were nearing their end to life besides improving and augmenting the INSAT system capacity. INSAT-3C is the second satellite of the INSAT-3 series. The first satellite, INSAT-3B was launched in March 2000.
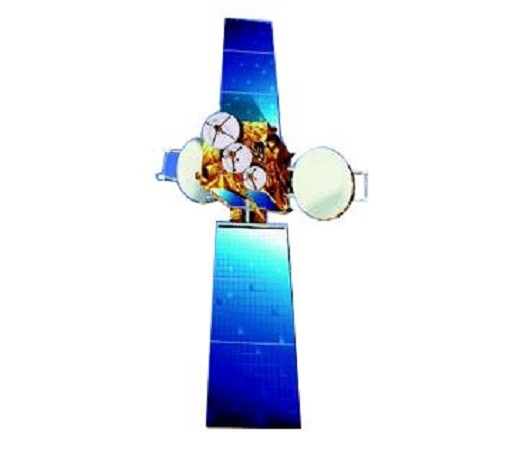

INSAT-3C
INSAT-3B
INSAT – 3B is the first of the five ISRO built satellites under INSAT – 3 series to join INSAT system. INSAT – 3B is collocated with INSAT – 2E at 83 deg East Longitude. This satellite primarily serves to business communication, mobile communication and developmental communication; It provides the first set to transponders for Swaran Jayanti Vidya Vikas Antariksh Upagraha Yojana (Vidya Vahini) for interactive training and developmental communication giving fillip to the training and developmental Communication channel of INSAT.
INSAT-3B
INSAT-2E
INSAT - 2E, the last of the INSAT -2 series of satellites built by ISRO, is a multi - purpose satellite for telecommunication, television broadcasting and meteorological services. The very High Resolution Radiometer operates in three spectral bands with 2 km resolution in visible band and 8km resolution in thermal infrared and water vapour bands. The water vapour band has been introduced in the INSAT system for the first time. In addition, INSAT - 2E also carries a Charge Coupled Device Camera, again for the first time in the INSAT. This camera also operates in three spectral bands - visible, near infrared and short wave infrared - providing a spatial resolution of 1 km.

INSAT-2E
INSAT-2D
INSAT-2D, identical to INSAT-2C, was launched on June 4, 1997 but the satellite became in-operable since October 4, 1997 following a power bus anomaly and associated problems. Hence it was replaced by in-orbit satellite, ARABSAT-1C, designated as INSAT-2DT.

INSAT-2D
INSAT-2C
Power of four C-band transponders increased to improve communication facilities in remote areas like Northeast and Andaman & Nicobar Islands. Coverage of two other C-band transponders is enlarged to include parts of Southeast Asia, Central Asia and West Asia

INSAT-2C
INSAT-2B
Insat-2B of the Insat-2 series of satellites built by ISRO, are multi-purpose satellites for telecommunication.

INSAT-2B
INSAT-2A
First Multipurpose satellite built by India, Successfully Operationalised in August 1992.It was used for Multipurpose Communication, meteorology and Satellite based search and rescue

INSAT-2A
INSAT-1D
The specification for the INSAT-1D is the same as the INSAT-1B but with expanded battery and propellant capacities, launched on 12 June 1990 to conclude the first generation INSAT series.

INSAT-1D
INSAT-1C
The INSAT-1C satellite was launched on 22 July 1988 from Kourou for location at 93.5°E to bring the INSAT system up to full capacity. Half of the 12 C-band transponders and its two S-band transponders were lost when a power system failure knocked out one of the two buses, but the meteorological earth images and its data collection systems were both fully operational.

INSAT-1C
INSAT-1B
When INSAT-1B was launched on 30 August 1983, it almost suffered the same fate as the INSAT-1A. It was not until mid-September that Ford and Indian controllers succeeded in deploying its solar array. By then it had been stationed at 74°E in place of INSAT-1A. Full operational capability was achieved in October 1983. It continued to operate into 1990 with all its 4375 two-way voice or equivalent circuits in use. Around 36,000 earth images were returned.

INSAT-1B
INSAT-1A
The Insat-1A was launched by a Delta in April 1982 but was abandoned in September 1983 when its attitude control propellant was exhausted.
INSAT-1A


